Diamond Price Prediction Using Machine Learning
A data science project analyzing 53,940 diamonds to build and evaluate regression models predicting price based on physical and quality attributes.
- Course
- Data Science Project, UT Austin
- Stack
- Python, Scikit-learn, XGBoost, Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Seaborn
Overview
This project examined how characteristics such as carat, cut, clarity, color, and dimensional volume influence price. Multiple machine learning models were trained and compared to understand driver importance and optimize predictive performance.
Can we accurately predict the price of a diamond using its physical and quality attributes?
Modeling Results
| Model | RMSE | R² |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | 1204.86 | 0.91 |
| Decision Tree (Pruned) | 1333.14 | 0.89 |
| Random Forest | 535.14 | 0.98 |
| XGBoost | 542.84 | 0.88 |
Random Forest produced the strongest performance with an R² of 0.98 and average prediction error (RMSE) of approximately $535.
Feature Insights
- • Carat and the engineered volume feature were the most influential price predictors
- • Clarity and color provided additional predictive power
- • Cut, depth, and table contributed minimally relative to size and quality features
Visualizations
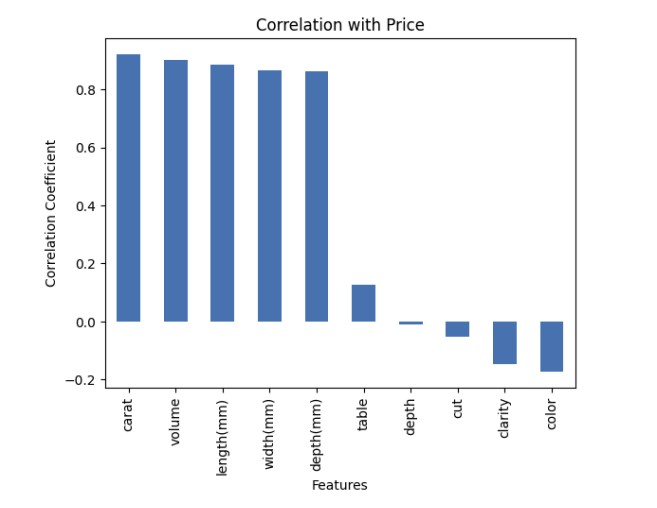
Feature importance ranking
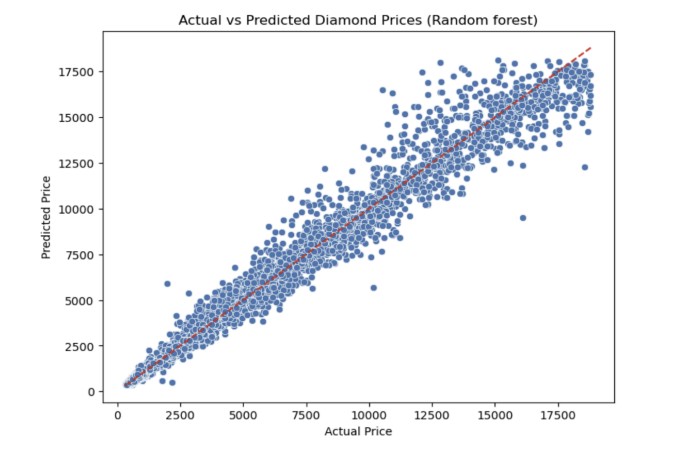
Random Forest actual vs predicted
Key Takeaways
- • Engineered features such as volume significantly improve model performance
- • Linear models struggle with nonlinear relationships common in pricing data
- • Tree-based ensembles capture complex interactions and offer superior accuracy